Hostwinds Tutorials
Search results for:
Table of Contents
Setup Remote Redis Server on Linux VPS
Redis is a flexible, high-performance database engine that supports complex operations and use-cases. You can set up a Redis server to run on your VPS and accept remote commands to modify, read, and perform operations on the database.
Step 1: Install the Redis backend.
RHEL / CentOS / Amazon Linux
sudo yum install Redis
Ubuntu / Debian
sudo apt-get install Redis-server
Fedora
sudo dnf -y install Redis.
Step 2: Start the Redis server backend service.
RHEL / CentOS / Amazon, Linux
sudo systemctl, start Redis
Ubuntu / Debian
sudo systemctl start Redis-server. service
Fedora
sudo systemctl start Redis
Step 3: Verify the Redis server is running
ps -aux | grep redis
You can also verify the server is handling requests by starting the Redis-cli and issuing the ping command.
redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> ping
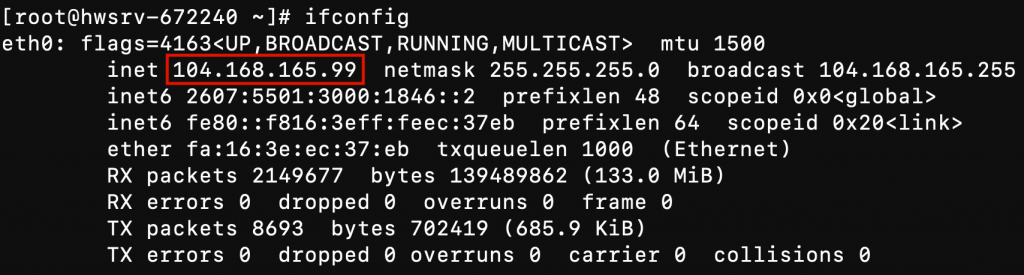
Step 4: Get public IPv4 address using ifconfig
ifconfig -a
Step 5: Bind the Redis server to your IPv4 address.
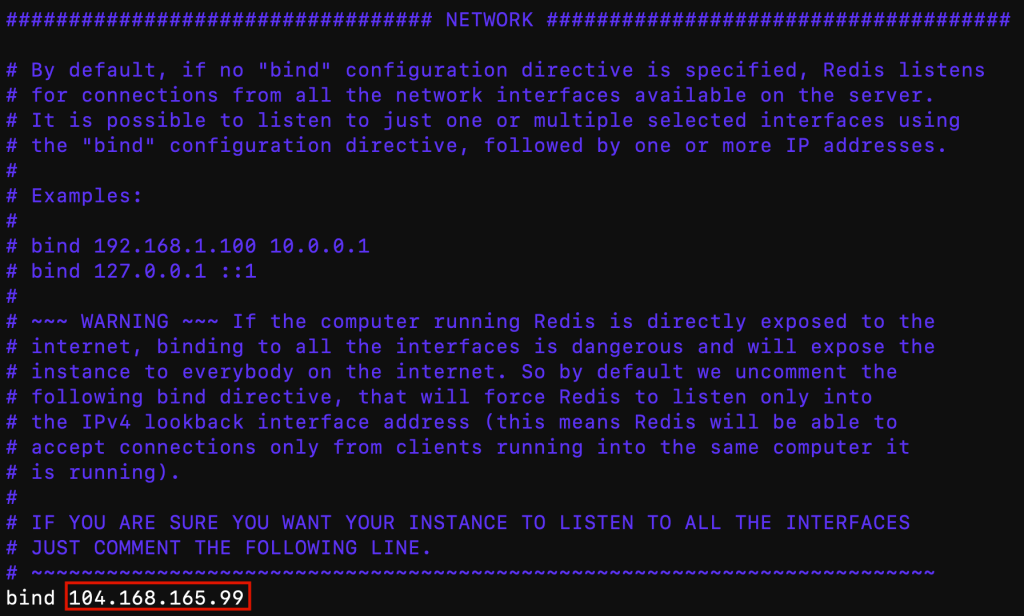
sudo vi /etc/redis.conf
By default, the Redis server will be bound to 127.0.0.1, which is only accessible from the server itself. To make the Redis server publicly accessible, you must bind the server to listen to the network interface associated with your public IPv4.
On line 66, modify bind 127.0.0.1 and replace the IP with your VPS IPv4.
Step 6: Restart Redis
RHEL / CentOS / Amazon Linux
sudo systemctl restart redis
Ubuntu / Debian
sudo systemctl restart Redis. service
Fedora
sudo systemctl restart Redis
Step 7: Verify external host access.
Verify the server can be accessed from an external host. Using the Redis-cli command on your local machine, you can provide the -h argument to connect to the remote Redis server that was just set up on your VPS.
redis-cli -h 104.168.165.99 104.168.165.99:6379> ping PONG
You are now able to access your Redis node on your VPS remotely.
Written by Hostwinds Team / April 10, 2020
